- Offerings
 Education benefits through TASC Universal Benefit Account® can help an employer stand out while investing in their workforce.
Education benefits through TASC Universal Benefit Account® can help an employer stand out while investing in their workforce. By providing financial security and removing the burden of unexpected expenses, these benefits contribute to both financial and mental well-being.
By providing financial security and removing the burden of unexpected expenses, these benefits contribute to both financial and mental well-being.Oversee all employee benefits administration for FSA, HSA, Dependent Care, plus 50 more benefit accounts all with ONE Portal, ONE Mobile App, and ONE Card.
TASC Offerings
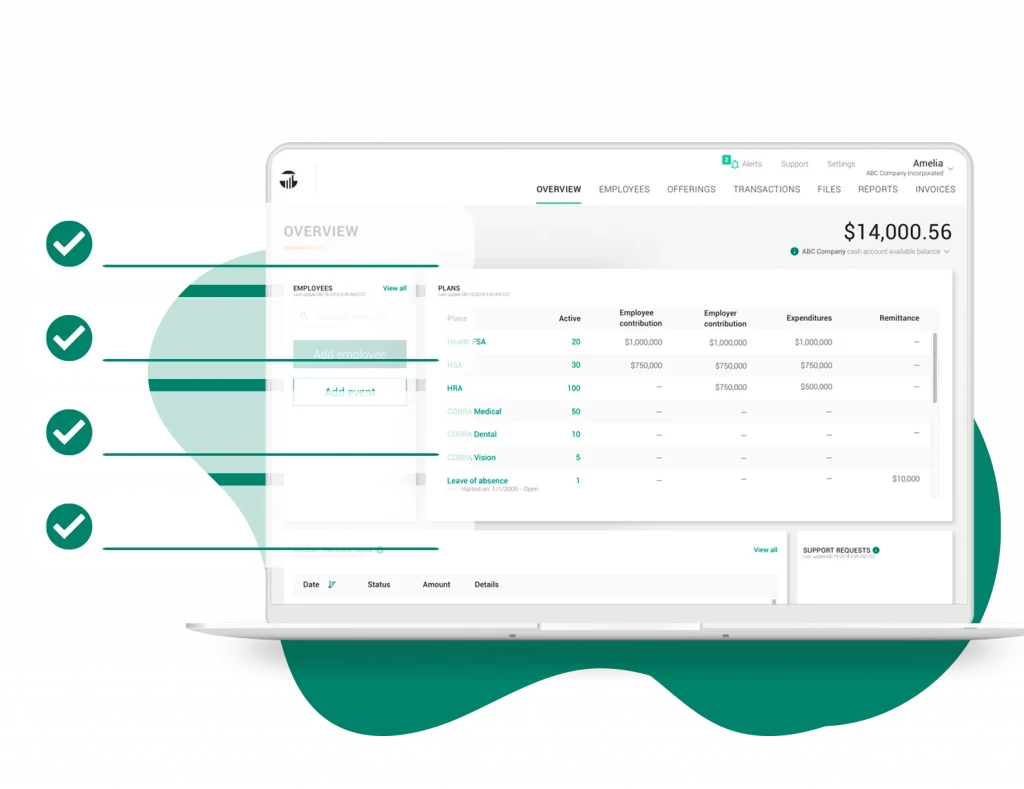
Get the advantages of one-stop-shopping for all of your employee benefit and compliance needs backed by outstanding customer care, innovative technology, and 45+ years of expertise.
From standard healthcare benefits like FSA, HSA and HRA to Family, Lifestyle, and COBRA, TASC offers the efficiency of a single platform and instant configurability.
- Partners
Employers
Learn how can you make the benefit experience easy and intuitive, save time and money and increase employee satisfaction through benefit account participation.
Distributors
Our distributors are a robust team of health insurance brokers, agents, tax professionals, and financial planners who help their clients handle benefits administration, continuation needs and compliance requirements.
Our Partners
Our goal is to provide wider access to comprehensive benefit options for both, employees and employers, through a network of businesses, brokers, and strategic partnerships.
Discover a solution that best fits your organization and become a part of the TASC network today.
- Resources
Blog
Read the latest industry news and browse benefit resources gathered by our team of experts. Subscribe to TASC Tracker to stay updated on compliance and benefit updates, plus more news impacting employers.
Eligible Expenses
Browse a list of FSA, HSA, HRA eligible expenses. Use your TASC Card to pay for healthcare-qualified expenses at clinics, optometrists, dentists, pharmacies and other merchants.
Benefit Limits
Regulatory limits allowed for each benefit account including Flexible Spending Accounts, Health Savings Accounts, Transportation Benefits, Qualified Small Employer HRA and Excepted Benefit HRA.
PLAN ADVISOR
With TASC’s Plan Advisor, current TASC clients now have access to an advisor, who can help you plan, select, and tackle important employee benefit account decisions as your business evolves.
Upcoming Webinars
Wednesday, September 17, 2025Maximizing Pre-Tax Benefits: Integrating FSAs, HSAs and Beyond
Wednesday, August 20, 20251.0 HRCI & 1.0 SHRM: Navigating the Sea of HRAs: Which Type of HRA Is Right for You?
Wednesday, July 23, 2025Essential Employee Benefits: The Top 10 Benefits for a Thriving Workforce
- About
About Us
With nearly 50 years of experience administering employee benefits for 80,000+ clients, TASC has a rich history in serving businesses of all sizes nationwide.
Leadership
Meet our officers and executives. Read their TASC journey and learn more about their positions at our organization.
Board of Advisors
TASC has gathered an outstanding group of individuals to carry out the mission and vision of our organization.
TASC Cares
We have a long-standing commitment to supporting our community and those less fortunate. We are privileged to share our success and give back to those in need.
Careers
We’re committed to making a difference for our clients and our employees. Join our team of over 700+ employees and experience the TASC difference.
About TASC
As the nation’s largest privately held third-party benefits administrator, TASC has a mission to improve the health, wealth and well-being of its customers, employees, and communities.